Discover all the geography and the most incredible ecosystems of Colombia. Desert, jungle, snowy peaks… discover a Colombia with varied landscapes…
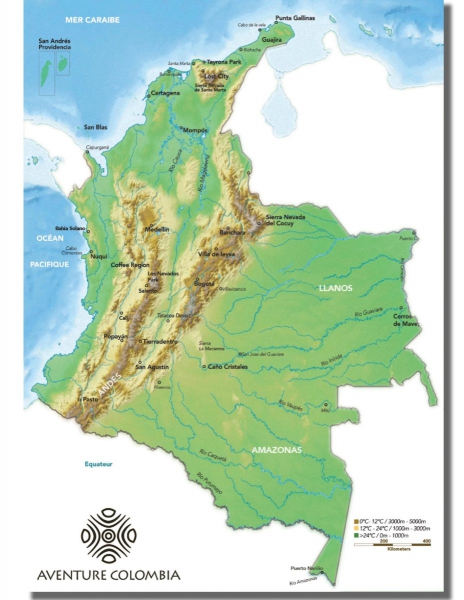
Colombia is a country located in the northwest of South America. It is the only country in South America where you can enjoy both the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans. Colombia has a population of just over 45 million and its main cities are Bogotá, the capital, Cali, Medellin, Bucaramanga, Barranquilla, Pereira and Cartagena.
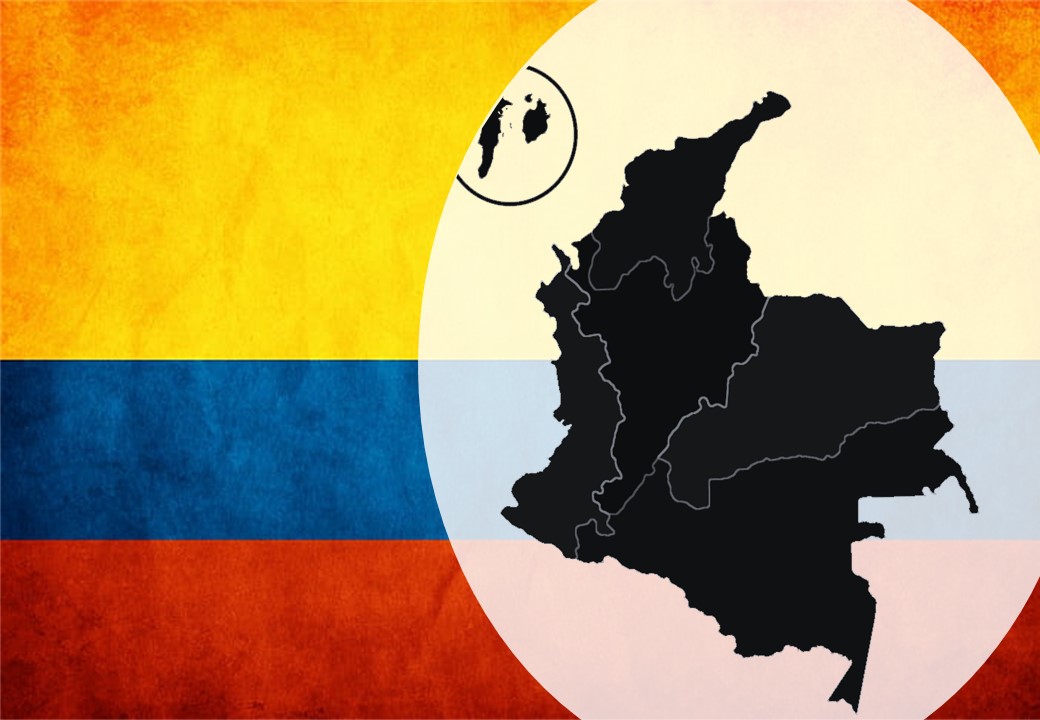
Colombia borders Venezuela and Brazil to the east, Peru and Ecuador to the south and Panama to the northwest. Colombia shares maritime borders with Panama, Costa Rica, Nicaragua, Honduras, Jamaica, Haiti, Dominican Republic and Venezuela by the Caribbean Sea and with Panama, Costa Rica, and Ecuador by the Pacific Ocean.
Colombia has mountains with the Andes, plains with the Llanos, tropical forests with the Amazon, and beaches with the Caribbean and the Pacific coast.
The mountain region: The Andes Mountains
The Andes mountain range extends from the north to the south of Colombia and occupies the west and center of Colombia. It is composed of 3 mountain ranges which are :
- the Eastern Cordillera,
- the Central Cordillera,
- the Western Cordillera.
The Andes mountain range penetrates Colombia through the department of Nariño, one of the departments with the largest coffee production in the country. This first range is called the Cordillera Occidental. The mountain range continues until the departments of Cauca and Huila, from where the other two mountain ranges are born.
These three mountain ranges, together with the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta and the Sierra de la Macarena constitute the topography of the country. The plains are located to the east of the Cordillera Oriental, to the west of the Cordillera Occidental and to the north of the country.
In the valley and the inter-Andean altiplanos we find :
- Los Llanos Orientales (Orinoquia and Amazonia)
- The Precambrian Orinoco Apaporis region
- The inter-Andean valleys of the Magdalena and Cauca rivers
- Aburrá valley
- Sinú valley
The main altiplanos are in:
- Ubaté valley
- Chiquinquirá valley
- Sogamoso valley
- The savannah of Bogotá
The Western Cordillera
Cauca and its indigenous communities, Cali and the Salsa, Risaralda and the coffee haciendas and the unexplored department of Choco. The Cordillera Occidental is a mountain range that varies in altitude from 1,500 meters at the Pacific coast to 3,960 meters in the region of Antioquia with Mount Paramillo. The mountain range creates a barrier between the Cauca Valley and the Pacific Coast. It also runs through the department of Antioquia.
The Central Mountain Range
Popayan and its colonial streets, the traditional dances in Nevia, the coffee region and Medellin. The Central Mountain Range rises to an average of 3,000 meters above sea level. Some mountain ranges like the Nevado del Huila reach 5,364 meters above sea level and the Nevado del Ruiz between Ibagua and Manizales reaches 5,311 meters above sea level. The incredible eternal snows are mostly found in this mountain range.
The Eastern Cordillera
The main cities of Colombia, lagoons, thermal baths, the great mountains of Boyaca, Santander and the peninsula of La Guajira.
The central mountain range separates the Magdalena Valley from the eastern plains. Here we find the greatest ascents and savannas. The Sumapaz paramo in the Bogotá savanna rises to 4,650 meters. The Sierra Nevada del Cocuy reaches 5,493 meters. The Cordillera cuts the north of the country. On one side it extends to Venezuela and on the other side it forms the Serrania del Perija, which descends to the west and meets one of the most beautiful deserts of the country in the peninsula of La Guajira.
The plains: the Orinoco region
Beyond the Andes, the eastern plain “llanos”, extends to the border with Venezuela along the rivers Arauca and Meta in the north. In the south, the plain extends to the border with Peru and Ecuador in the department of Putumayo. Finally, it extends from the base of the Cordillera Oriental to the Orinoco. This region is divided into two natural landscapes: the Amazon rainforest in the south of Colombia and the eastern plains in the center of the country.
An isolated mountain system
About 100 kilometers from Villavicencio is La Macarena, a special tropical ecosystem that hosts the Sierra Nevada de la Macarena and the river of seven colors: Caño Cristales.

Colombia’s water resources
Colombia has abundant water resources, represented by :
- The ocean waters of the Caribbean Sea and the Pacific Ocean that bathe the country respectively by the north and the west.
- The lacustrine waters are constituted mainly by lakes and swamps. For example, the lagoon of Tota in Boyaca, the lagoon of Fuquene in Cundinamarca and the lagoon of Guatavita among others. The largest of the wetlands is the Ciénaga Grande de Santa Marta.
- From the underground waters are born the springs and accumulate high temperatures in the thermal baths. The most famous thermal baths are the ones in Boyaca, Puracé in Cauca, Nevado del Ruiz, Santa Rosa de Cabal and others in Cundinamarca.

Natural regions and their corresponding tourist activities
Colombia has five natural regions and one island region where the same characteristics of relief are found, between mountainous and flat landscapes. We also find the same characteristics of climate, which vary according to the seasons, between rainy season and dry season, and according to the distance from the sea. It is the same for the vegetation and the soil conditions.
Amazon: nature reserves and ecotourism
This region includes the departments of Caquetá, Putumayo, Amazonas, Vaupés, Guainía and Guaviare, and represents the international land borders with Venezuela, Brazil, Peru and Ecuador.
It is a flat region, with high rainfall and temperatures. It is composed by immense tropical forests that host an incredible biodiversity. It is crossed by several abundant rivers such as Caquetá, Putumayo, Vaupés and Apaporis. The main cities of this region are Florencia, Leticia, Mocoa, San José del Guaviare and Mitú. The indigenous communities are mainly present in the departments of Guainía, Vaupés and Amazonas.

The Andean region: extreme sports and family activities
The Andean region is composed of the three Andes mountain ranges and concentrates 70% of the population and the economic and urban centers of Bogotá, Medellín, Cali, Bucaramanga, Cúcuta, Manizales, Pereira, Armenia, Ibagué, Neiva, Popayán, Pasto and Tunja. The departments are Nariño, Cauca, Valle del Cauca, Huila, Tolima, Quindío, Risaralda, Caldas, Chocó, Antioquia, Cundinamarca, Boyacá, Santander, Norte de Santander, Meta, Córdoba, César, Arauca, Caquetá, Casanare and Putumayo. This region has a great climatic diversity due to its high altitude.
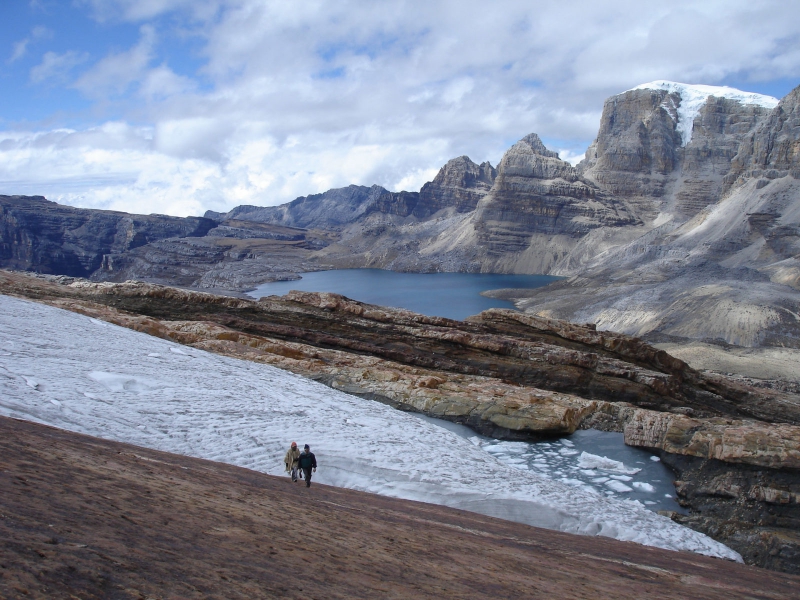

The Caribbean region: water sports, beaches and treks
The Caribbean region extends from the northeast of the Gulf of Uraba to the Guajira Peninsula, and from the foothills of the Western and Central Cordilleras to the beaches of the Caribbean Sea.
It is a flat region, crossed by numerous rivers and swamps. It has the closest snow-capped mountains to the sea in the world. The Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta is a mountainous area with a great climatic and natural diversity, where we find the highest peaks of the country.
The departments of the Caribbean region are La Guajira, Bolívar, Atlántico, Cesar, Magdalena, Sucre, Córdoba, Santander and Antioquia.
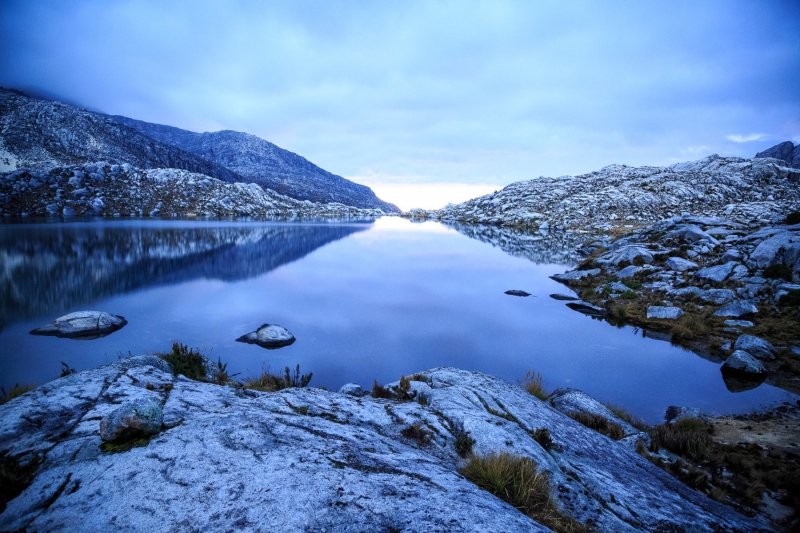

The Orinoco region: Inirida River, myths and legends
Known as the “eastern Llanos“, this region extends from the foothills of the eastern mountain range to the border with Venezuela and between the Arauca River in the north and the Guaviare River in the south. The region includes as departments: Arauca, Casanare, Guainía, Meta, Guaviare, Vaupés and Vichada.
It is characterized by vast savannahs irrigated by numerous and abundant rivers. Most of the inhabitants of this region live in Villavicencio, Arauca, Puerto Carreño, Acacias, Puerto Lopez, Yopal and San Martin. The indigenous communities Tunebos, Betoyes, Sikuanis, U’wa, Curripaco, Puinaves, Piapocos and Guahibos represent about 5% of the population.
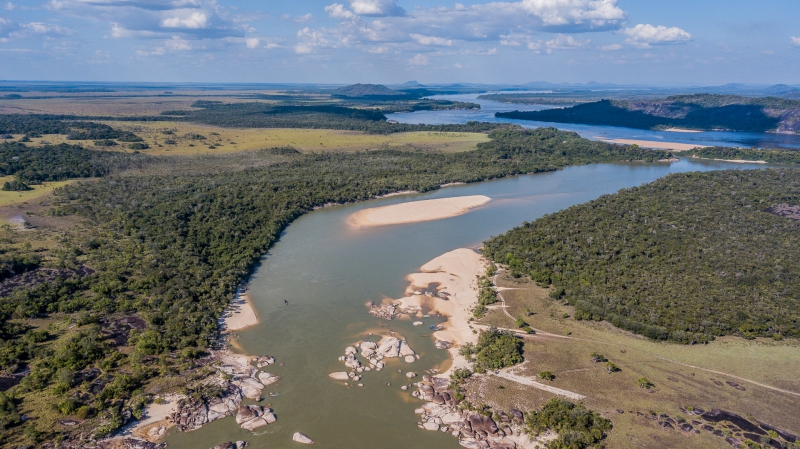

The Pacific region: whale watching and exuberant nature
Located in the western zone of Colombia, the region extends from the Gulf of Uraba, bordering Panama in the north, to the border with Ecuador in the south. The region is bounded by the Cordillera Occidental in the east and by the Pacific coastline in the west. The Pacific region contains the following departments: Nariño, Cauca, Valle del Cauca, Antioquia y almost the entire department of Chocó.
This region is very humid and has vast mangroves and swamps. With the highest rainfall in the world, the Pacific region is home to many abundant rivers such as the Atrato, San Juan, Patía, Baudó, Mira, Iscuandé, Micay, Telembí, Anchicayá, Naya, Calima, Timbiquí, Dagua and Yurumanguí. It also has the largest concentration of Afro-Colombian and indigenous communities in this Pacific region.

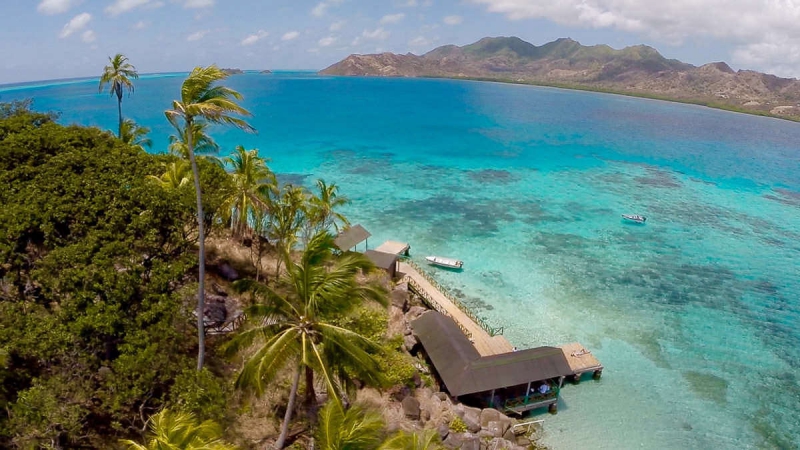
The island region: sun, beach and relaxation
Colombia is an island state with many islands. In the Caribbean, we find the Ciénaga of Santa Marta, the islands of Rosario and San Bernardo. There are also the islands of Baru and Tierrabomba. These islands border the city of Cartagena de Indias.
Other islands such as San Andrés, Providencia and Santa Catalina, the sandbanks of Alicia, Quitasueño, Serrana and Serranilla, and a series of rocky islands such as Roncador and Albuquerque, are further away from the mainland. The island of Malpelo, for example, is located 400 km from the coast.

Map Colombia, geography of Colombia
Contact a Travel Agent now
Design the trip of your dreams today with one of our country experts: